- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- 62-193 Technology Literacy for Educators Dumps
Pass Microsoft MCE 62-193 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


62-193 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 41 Questions & Answers. Last update: Jan 31, 2026
- Training Course 45 Video Lectures
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.
All Microsoft MCE 62-193 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 62-193 Technology Literacy for Educators practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Microsoft 62-193 Exam: A Pathway to Technology-Driven Teaching Excellence
The Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 exam is designed to validate the essential technology competencies required for modern educators. This certification examines how educators apply information and communication technologies to create rich, effective, and engaging learning experiences. Unlike exams that test proficiency with specific software tools, this certification emphasizes understanding how to integrate digital resources into teaching practice in meaningful ways. The exam is appropriate for pre-service teachers, faculty members, and in-service educators aiming to strengthen their instructional use of technology and enhance student learning outcomes.
Technology literacy in education is no longer optional; it is a fundamental requirement in classrooms where digital tools influence collaboration, creativity, and problem-solving. The 62-193 exam provides a structured framework for educators to demonstrate their ability to leverage technology to facilitate learning across six major domains, ensuring that technology use aligns with pedagogical goals and supports students’ development of critical 21st-century skills.
Understanding the Exam Structure and Format
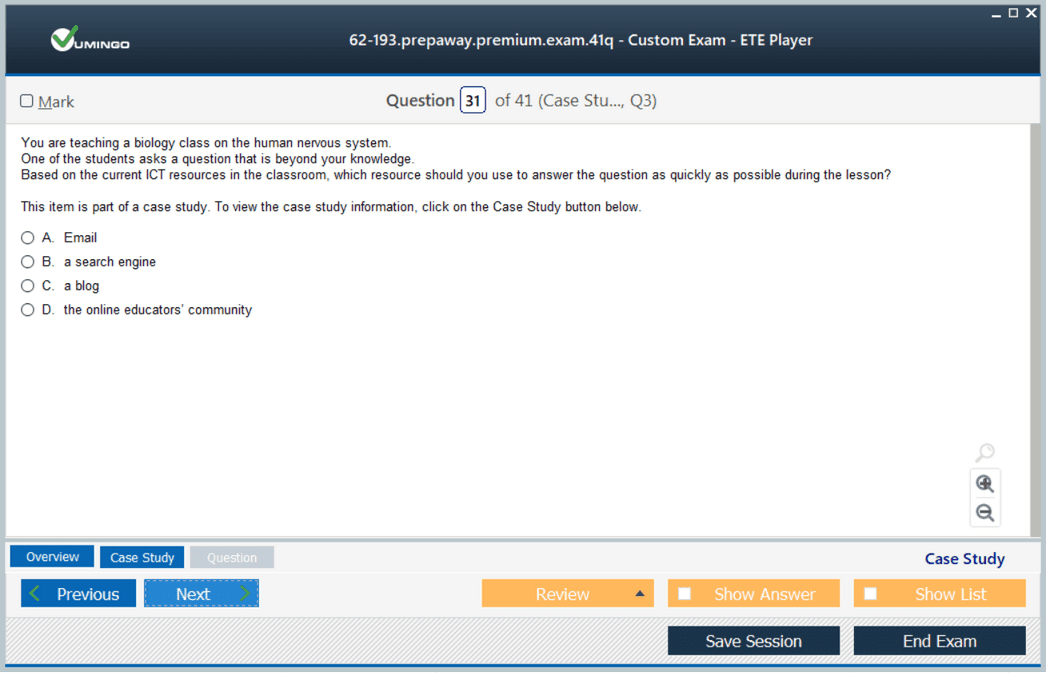
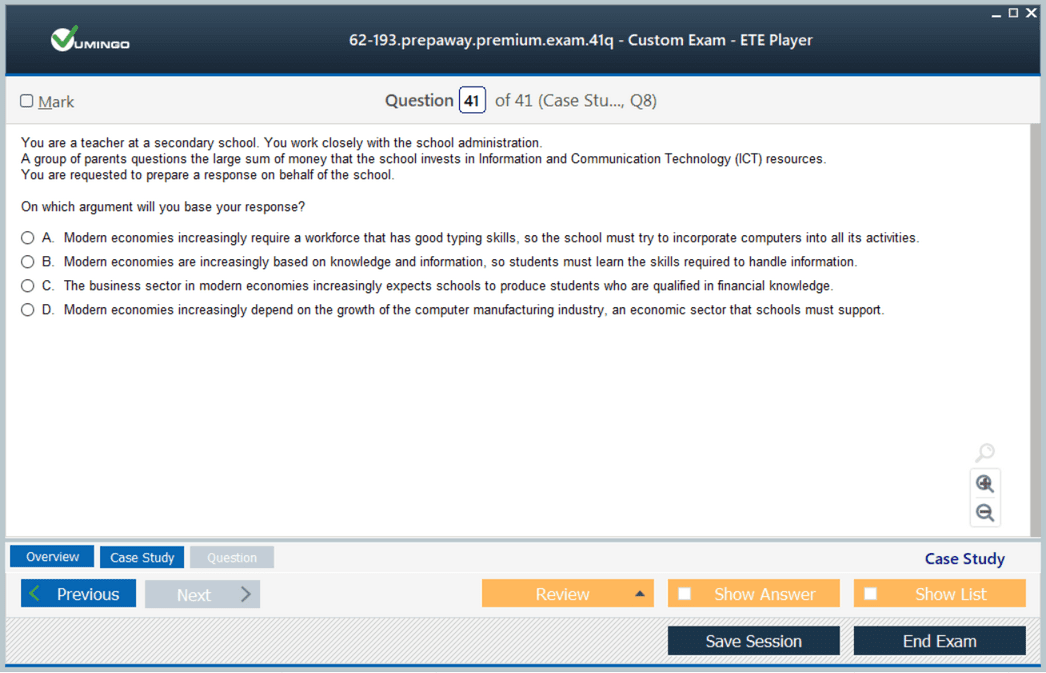
The 62-193 exam is an intermediate-level certification designed to reflect realistic classroom and instructional scenarios. The exam typically consists of 40 to 60 questions, which may include multiple-choice, multi-selection, and true/false formats. The time allocated for completing the exam is 90 minutes, and the passing score is set at 70. These specifications indicate the exam’s focus on both knowledge comprehension and practical application of technology integration strategies. The questions are constructed to test an educator’s ability to analyze scenarios, plan interventions, and apply ICT tools to achieve specific learning outcomes.
The exam does not require candidates to demonstrate skill in a particular software application. Instead, it focuses on how educators perceive, interpret, and apply technology concepts within a pedagogical context. Candidates are assessed on their understanding of educational strategies that utilize technology to support collaboration, communication, problem-solving, self-regulation, and knowledge construction.
Core Competencies Evaluated in the 62-193 Exam
The 62-193 exam evaluates educators’ competencies across six main domains that are essential for effective technology integration. These domains serve as a guide for how educators can incorporate digital tools into daily teaching practice and measure the impact of technology on student learning.
Facilitating student collaboration involves the use of digital platforms and tools to encourage group work, peer learning, and shared knowledge creation. Educators are expected to demonstrate the ability to organize activities where students can interact, exchange ideas, and co-create solutions to problems using digital resources.
Facilitating skilled communication assesses an educator’s ability to help students convey ideas clearly and effectively using technology. This includes guiding students to present information through digital mediums, participate in online discussions, and collaborate in environments where communication is enhanced by technology.
Facilitating knowledge construction focuses on the ability of educators to support students in developing understanding, analyzing information, and constructing new knowledge using digital tools. This competency encourages inquiry-based learning and helps students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills by integrating technology into research, analysis, and project-based activities.
Facilitating self-regulation examines how educators can guide students to plan, monitor, and evaluate their own learning through technology. This domain emphasizes teaching students to use digital tools for goal-setting, time management, self-assessment, and reflection on learning progress.
Facilitating real-world problem solving and innovation measures an educator’s capability to use technology to connect classroom learning with practical challenges. This includes helping students identify problems, explore solutions, and implement innovative strategies using digital resources. The domain encourages creativity and critical thinking by providing opportunities for students to apply learning in realistic scenarios.
Facilitating student use of information and communication tools emphasizes ensuring that students are proficient in using digital tools effectively and responsibly. Educators are expected to guide students in selecting appropriate technologies for tasks, using tools efficiently, and applying skills ethically to support academic and collaborative work.
The Importance of Technology Literacy for Educators
Technology literacy is a key component of modern teaching. Educators who are proficient in integrating technology can enhance instructional design, create dynamic learning environments, and support diverse learning styles. The 62-193 exam highlights the value of educators understanding not just how to use digital tools, but how to embed them meaningfully into the curriculum. By developing technology literacy, educators are better positioned to facilitate active learning, encourage student engagement, and improve learning outcomes across multiple subject areas.
This competency is especially critical in an era where students have increasing access to information and digital tools outside the classroom. Educators must not only teach content but also help students navigate digital resources, critically evaluate information, and collaborate effectively online. The 62-193 exam emphasizes these aspects, preparing educators to respond to the evolving demands of technology-enhanced education.
Preparing for the Microsoft 62-193 Exam
Effective preparation for the 62-193 exam requires a combination of theoretical understanding and practical application. Familiarity with the six content domains is essential. Educators should analyze case studies, participate in instructional simulations, and reflect on their experiences using technology to support learning. Preparation strategies may include reviewing frameworks for digital literacy in education, exploring practical classroom applications of ICT tools, and evaluating how technology can support diverse learners.
Practical experience is crucial for internalizing these competencies. Educators can create lesson plans that incorporate collaborative tools, virtual learning environments, and digital assessments. Implementing these practices allows candidates to experience the challenges and benefits of technology integration firsthand, building confidence in applying their knowledge during the exam.
Collaborative study approaches can also enhance preparation. Engaging in discussions with peers, sharing experiences, and analyzing different strategies for integrating technology encourages critical thinking and reinforces understanding of the content domains. This approach reflects the collaborative nature of modern education, where teachers continuously learn from one another and refine their practices based on feedback and reflection.
Utilizing Practice Scenarios and Simulation Exercises
Practice scenarios and simulation exercises are highly effective for exam readiness. By working through realistic classroom scenarios, educators can apply knowledge from the six content domains and develop problem-solving skills that are directly relevant to the exam. These exercises also help educators develop a strategic approach to managing time, interpreting questions, and applying technology concepts to achieve specific instructional goals.
Simulation exercises encourage candidates to consider multiple factors when integrating technology, such as student engagement, accessibility, and learning outcomes. This level of preparation aligns closely with the practical orientation of the 62-193 exam, which prioritizes the ability to use technology strategically rather than simply demonstrating procedural skills.
Continuous Professional Development and Lifelong Learning
The 62-193 exam also emphasizes the importance of continuous professional development. Technology in education evolves rapidly, and educators must continually update their knowledge and skills to remain effective. Achieving this certification demonstrates a commitment to lifelong learning and positions educators to adapt to new tools, methodologies, and pedagogical approaches. It reinforces the principle that technology integration is an ongoing process that requires reflection, experimentation, and iterative improvement.
By cultivating technology literacy, educators can create inclusive, innovative, and adaptive learning environments. This approach not only supports student success but also enhances professional satisfaction by empowering educators to implement best practices and see tangible results in the classroom.
The Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 exam provides a comprehensive assessment of an educator’s ability to integrate technology meaningfully into instruction. It evaluates competencies across collaboration, communication, knowledge construction, self-regulation, problem-solving, and ICT usage. Preparation involves both theoretical study and practical application, emphasizing the real-world integration of digital tools in teaching. Achieving this certification validates educators’ technology literacy, supports professional growth, and enables the creation of engaging and effective learning experiences for students. By developing these skills, educators are better equipped to meet the demands of modern education and support student success in a digitally rich learning environment.
Preparing Effectively for the Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 Exam
Successfully preparing for the Microsoft 62-193 exam requires a combination of theoretical understanding, practical application, and reflective learning. This exam evaluates an educator’s ability to integrate technology into the classroom in a meaningful way, emphasizing pedagogical effectiveness rather than simply operational knowledge of tools. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in six content domains and the ability to apply these skills in realistic teaching scenarios. Preparation begins with understanding the exam objectives, identifying areas of strength and weakness, and creating a study plan that ensures balanced coverage of all essential topics.
A strategic approach to exam preparation includes dedicating specific time blocks for study, hands-on practice, and review of assessment results. Since the exam emphasizes scenario-based problem solving, candidates should focus on understanding how to apply digital literacy concepts to real classroom challenges. Effective preparation bridges the gap between knowing technology and applying it to enhance learning outcomes.
Understanding the Six Content Domains in Depth
The Microsoft 62-193 exam is built around six critical content domains that assess how educators integrate technology in their teaching. Facilitating student collaboration requires understanding how digital tools can encourage teamwork, shared learning, and peer-to-peer interaction. Candidates should explore platforms that allow students to communicate, co-create content, and collaborate on projects while also understanding strategies to monitor and assess collaborative engagement effectively.
Facilitating skilled communication involves guiding students to convey ideas clearly and accurately using digital media. Educators need to focus on teaching methods that enable students to create presentations, participate in online discussions, and document their learning in interactive formats. Understanding the nuances of digital communication, including accessibility, clarity, and audience engagement, is essential to this domain.
Facilitating knowledge construction evaluates an educator’s ability to help students process, analyze, and synthesize information using technology. Candidates must demonstrate strategies for promoting inquiry-based learning, integrating research tools, and supporting students in creating knowledge products such as reports, multimedia projects, and interactive presentations. The goal is to foster an environment where students actively construct understanding rather than passively receiving information.
Facilitating self-regulation focuses on how educators use technology to support students in monitoring their own learning. This includes setting goals, tracking progress, using feedback tools, and reflecting on performance. Candidates need to understand methods to encourage students to become independent learners who can assess their own work and adjust strategies to improve outcomes.
Facilitating real-world problem solving and innovation assesses the use of technology to connect classroom learning with practical challenges. Educators are expected to design activities that encourage students to apply knowledge to solve problems, innovate, and develop critical thinking skills. This domain emphasizes creativity and practical application, enabling students to engage with learning in authentic contexts.
Facilitating student use of information and communication tools requires guiding students to use digital tools effectively and responsibly. Candidates should demonstrate understanding of digital literacy, ethical use of technology, and strategies to help students select appropriate tools for academic and collaborative purposes. This domain ensures that technology integration is purposeful, ethical, and aligned with learning objectives.
Practical Methods for Exam Preparation
Effective preparation for the 62-193 exam combines theory and practice. Candidates should engage in experiential learning by designing lesson plans that integrate technology across the six domains. For example, they can create collaborative projects using shared digital workspaces, develop multimedia presentations to enhance communication, or implement digital tools that support self-assessment and reflection. Experiential practice allows candidates to understand the implications of technology decisions on student engagement and learning outcomes.
Analyzing case studies of technology integration is another effective approach. Candidates can review scenarios from classrooms where digital tools were implemented, identify challenges, and evaluate strategies for improvement. This analysis helps candidates anticipate potential classroom situations they may encounter in the exam and understand how to apply digital literacy skills in context.
Collaborative preparation can reinforce learning. Working with peers to discuss concepts, share experiences, and develop teaching strategies enhances understanding and retention of material. Collaborative study also reflects the principles tested in the exam, where educators are expected to foster student collaboration and communication through technology.
Leveraging Practice Exercises and Simulations
Practice exercises and simulation tools are essential for preparation. Candidates can create interactive assignments, quizzes, and project-based exercises to evaluate their understanding of the six content domains. This approach not only strengthens knowledge but also helps candidates become familiar with the types of questions and scenarios they will face in the exam.
Simulation exercises replicate real classroom experiences, allowing candidates to test technology integration strategies under realistic conditions. For instance, they can design a collaborative project in a digital environment, monitor student participation, and provide feedback. This hands-on practice ensures that candidates are comfortable applying concepts to practical teaching situations, which is a core focus of the exam.
Self-assessment is a crucial component of preparation. Candidates should reflect on their teaching practices and document experiences integrating technology. Keeping records of lesson plans, classroom activities, and outcomes helps internalize knowledge and ensures readiness for scenario-based questions. This process strengthens both conceptual understanding and the ability to apply technology strategically.
Integrating Technology in Diverse Learning Environments
Candidates must understand how technology functions across different learning contexts. Traditional classrooms, blended learning environments, and fully digital classrooms each present unique challenges and opportunities. Adapting teaching strategies to fit these contexts is essential for both exam readiness and real-world application.
Accessibility considerations are also critical. Candidates need to ensure that technology integration supports learners with diverse needs. Knowledge of assistive technologies, accessible content formats, and inclusive digital practices ensures that all students can engage meaningfully with learning resources. The exam evaluates an educator’s ability to implement technology in a way that is equitable and effective for all learners.
Applying Frameworks for Technology Integration
Frameworks such as TPACK and SAMR are valuable tools for structuring technology integration. The TPACK model emphasizes the intersection of technological, pedagogical, and content knowledge, guiding educators to make informed decisions about tool selection and instructional design. The SAMR model helps candidates evaluate whether technology is merely substituting traditional methods or transforming learning experiences.
Understanding and applying these frameworks during preparation enables candidates to approach exam scenarios with a systematic methodology. They can analyze lesson plans, identify opportunities for enhancing learning with technology, and justify their instructional decisions. This depth of understanding aligns with the scenario-based approach of the 62-193 exam.
Critical Thinking and Analytical Skills
The 62-193 exam emphasizes critical thinking and problem-solving abilities in educational technology contexts. Candidates must analyze scenarios, identify challenges, and propose solutions using technology. Developing these skills requires reflection on teaching practices, evaluation of tool effectiveness, and consideration of student engagement and outcomes.
Reflective practice enhances analytical skills. Candidates should ask questions such as how technology affects learning, whether it supports collaboration and creativity, and how it addresses diverse student needs. Documenting reflections and reviewing solutions strengthens the ability to respond effectively to complex scenarios in the exam.
Time Management and Exam Strategy
Time management is an essential component of exam preparation and performance. Candidates should allocate sufficient study time to each content domain, practice answering scenario-based questions, and simulate exam conditions to improve pacing. Developing a strategy for interpreting questions, prioritizing tasks, and allocating time efficiently during the exam enhances accuracy and reduces anxiety.
Familiarity with question formats is also important. Understanding how to approach multiple-choice, multi-selection, and true/false questions, as well as scenario-based items, allows candidates to respond effectively. Practicing under timed conditions builds confidence and ensures that candidates can apply knowledge efficiently during the exam.
Continuous Professional Development
Preparing for the 62-193 exam is part of a broader commitment to professional growth. Technology in education evolves rapidly, and educators must continually update skills to remain effective. This exam encourages lifelong learning by emphasizing the ongoing development of technology integration strategies, reflective teaching practices, and digital literacy competencies.
Achieving the certification demonstrates an educator’s readiness to adopt innovative instructional strategies, improve student engagement, and support meaningful learning outcomes. It also positions candidates to stay informed about emerging technologies and trends, ensuring that their teaching practices remain relevant and effective in changing educational contexts.
Effective preparation for the Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 exam requires a multifaceted approach that combines theoretical study, practical application, reflective practice, and strategic exam techniques. Candidates must develop a deep understanding of six content domains, apply technology integration frameworks, adapt strategies to diverse learning environments, and cultivate critical thinking and analytical skills. Leveraging practice exercises, simulations, collaborative study, and reflective documentation ensures that candidates are well-prepared for scenario-based questions and real-world application. By mastering these strategies, candidates are positioned not only to succeed in the exam but also to enhance instructional effectiveness, support student learning, and promote lifelong learning in technology-rich educational environments.
Integrating Technology in Lesson Planning for Microsoft 62-193 Exam
Effective preparation for the Microsoft 62-193 exam involves more than understanding theoretical concepts; it requires demonstrating practical application in classroom contexts. Lesson planning serves as a key method for integrating technology into teaching and assessing readiness for scenario-based exam questions. Educators must consider how to design lessons that actively engage students, foster collaboration, and support critical thinking. The focus should be on embedding technology seamlessly into instruction rather than using it as an isolated tool. Candidates can start by identifying learning objectives aligned with curriculum standards and then determining which technology tools best support achieving those objectives.
Incorporating digital platforms such as collaborative workspaces, multimedia content creation tools, and virtual assessment systems allows students to engage actively with learning materials. When designing lessons, it is essential to consider how each tool enhances the learning process. For example, using collaborative platforms can promote teamwork in project-based activities, while interactive multimedia can clarify complex concepts and facilitate deeper understanding. Candidates preparing for the 62-193 exam should be able to articulate why certain tools are chosen and how they contribute to student learning outcomes.
Designing Collaborative Activities
Collaboration is a central focus of the 62-193 exam, and educators must demonstrate strategies to promote teamwork using technology. Designing collaborative activities requires careful planning to ensure meaningful participation from all students. Tools such as online discussion boards, shared documents, and virtual project spaces allow students to work together, share ideas, and provide feedback. Effective collaboration strategies include assigning roles within groups, setting clear expectations, and monitoring contributions to maintain equitable engagement.
Candidates should practice designing collaborative tasks that address real-world problems or interdisciplinary projects. This approach encourages students to develop critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills while using technology effectively. In preparation for the exam, candidates can simulate these activities, analyze student interactions, and refine methods for facilitating digital collaboration.
Enhancing Communication Skills Through Technology
Communication is a vital component assessed in the 62-193 exam. Candidates must understand how to guide students in expressing ideas clearly, using digital media to enhance clarity, engagement, and accessibility. Educators can incorporate presentation tools, multimedia content creation, and discussion forums to strengthen communication skills. When planning lessons, it is important to provide opportunities for students to share their understanding, explain reasoning, and collaborate on content creation.
Practical exercises can include having students create digital presentations on assigned topics, engage in online debates, or produce instructional videos. These activities develop students’ abilities to organize thoughts, convey information effectively, and adapt communication to different audiences. Candidates preparing for the exam should practice implementing these strategies and evaluating their effectiveness in improving student communication outcomes.
Applying Knowledge Construction Strategies
Facilitating knowledge construction is another key domain in the 62-193 exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to support students in processing, analyzing, and synthesizing information using technology. Lesson planning should integrate inquiry-based learning, project-based tasks, and research activities that encourage students to construct their own understanding. Digital tools such as content management systems, online research databases, and collaborative note-taking platforms can support these activities.
Candidates can practice designing scenarios where students explore questions, gather information, and create knowledge products such as reports, digital portfolios, or multimedia presentations. Reflecting on these experiences helps candidates understand how technology facilitates deeper learning and how to address challenges such as information overload, source evaluation, and effective collaboration.
Promoting Self-Regulated Learning with Technology
The 62-193 exam emphasizes the importance of supporting student self-regulation. Educators must demonstrate strategies to help students plan, monitor, and evaluate their learning. Technology can play a key role in this domain through digital goal-setting tools, learning management systems, and self-assessment platforms. Lesson planning should include opportunities for students to track progress, set personal objectives, and reflect on learning experiences.
Candidates can create exercises where students maintain digital journals, use progress tracking dashboards, or complete reflective surveys. By analyzing student engagement and outcomes, candidates gain insights into how technology supports independent learning. This hands-on approach strengthens preparation for exam questions that assess understanding of self-regulated learning strategies.
Encouraging Real-World Problem Solving and Innovation
Real-world problem solving and innovation is a core focus of the 62-193 exam. Educators must design lessons that connect classroom learning to practical challenges, allowing students to apply knowledge in meaningful ways. Candidates can develop project-based activities where students identify problems, propose solutions, and use technology to implement and evaluate their ideas. This approach promotes critical thinking, creativity, and analytical skills.
Simulated scenarios can include tasks such as designing sustainable solutions for local community issues, developing digital campaigns, or creating prototypes using virtual tools. Candidates preparing for the exam should practice guiding students through these processes, monitoring progress, and evaluating outcomes to demonstrate mastery of problem-solving strategies.
Leveraging Information and Communication Tools
The 62-193 exam assesses an educator’s ability to facilitate student use of information and communication tools. Candidates must ensure students can select appropriate tools, use them effectively, and apply digital literacy principles. Lesson planning should incorporate activities that require students to research, analyze, and communicate using various technologies.
Examples include using collaborative documents for group projects, designing interactive multimedia presentations, and employing data visualization tools for analysis. Candidates should practice guiding students in responsible technology use, ethical research practices, and evaluating digital resources critically. Developing these skills ensures students can navigate complex information environments and supports readiness for exam scenarios focused on digital literacy.
Integrating Assessment and Feedback Mechanisms
Effective lesson planning includes strategies for assessment and feedback using technology. Candidates must design activities that provide opportunities for formative and summative assessment, ensuring students receive timely and meaningful feedback. Digital tools such as online quizzes, collaborative annotation platforms, and automated feedback systems enhance assessment practices and support continuous learning.
Candidates can simulate assessment scenarios, analyze student responses, and refine feedback strategies. Preparing for the 62-193 exam involves understanding how assessment aligns with instructional goals, how technology can support evaluation, and how feedback can enhance student engagement and performance.
Scenario-Based Practice for Exam Readiness
Scenario-based practice is critical for success in the 62-193 exam. Candidates should work through realistic teaching situations where they must apply knowledge from all six content domains. This may include designing a technology-integrated lesson plan for a specific subject, facilitating online collaboration, or addressing challenges in digital communication. By analyzing scenarios, proposing solutions, and reflecting on outcomes, candidates strengthen critical thinking and application skills.
Simulation exercises can include managing virtual classroom activities, troubleshooting technology-related challenges, or evaluating the effectiveness of instructional strategies. Practicing these scenarios helps candidates develop confidence and prepares them to respond effectively to the complex, real-world problems presented in the exam.
Developing Reflective Practices
Reflective practice is essential for both exam preparation and professional growth. Candidates should maintain records of lesson planning, technology integration, and student outcomes. Reflecting on successes, challenges, and areas for improvement allows candidates to refine teaching strategies and deepen understanding of technology’s role in learning. Reflection also supports adaptive teaching practices, ensuring educators can adjust approaches based on student needs, engagement levels, and performance data.
Preparing for the 62-193 exam involves documenting reflections, analyzing results, and applying insights to future scenarios. This process not only reinforces knowledge but also demonstrates readiness to apply technology strategically in teaching contexts.
Managing Time and Exam Strategy
Time management is a critical component of both preparation and exam performance. Candidates should allocate sufficient study periods to cover all content domains, practice scenario-based exercises, and review reflective notes. Developing a strategy for approaching different question types, such as multiple-choice, multi-selection, and scenario-based items, enhances efficiency and accuracy during the exam.
Simulating exam conditions helps candidates manage time effectively and reduces anxiety. Practicing under timed conditions ensures familiarity with pacing, question interpretation, and application of knowledge to real-world scenarios. Developing a clear strategy improves confidence and ensures candidates can perform optimally during the exam.
Leveraging Professional Development Opportunities
The 62-193 exam encourages candidates to engage in continuous professional development. Exploring workshops, webinars, and collaborative learning opportunities strengthens understanding of technology integration strategies. Candidates should focus on learning from peers, observing best practices, and experimenting with new tools to enhance instructional approaches. Professional development supports exam readiness by providing exposure to diverse methods of applying technology in education.
Continuous learning also ensures educators remain current with emerging tools and trends. Preparing for the 62-193 exam through professional development activities fosters adaptive teaching practices and reinforces the practical application of technology literacy concepts.
Connecting Exam Preparation to Real-World Application
Preparing for the 62-193 exam is closely aligned with improving real-world teaching practices. Candidates develop skills that are directly applicable to classroom instruction, such as designing collaborative activities, facilitating communication, supporting knowledge construction, and promoting self-regulated learning. By integrating these strategies into daily practice, educators enhance student engagement, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities.
Candidates can create portfolios documenting lesson plans, technology use, and student outcomes. This documentation demonstrates practical application of knowledge, supports reflective learning, and strengthens readiness for exam scenarios.
Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 exam emphasizes practical application, lesson planning, and classroom scenarios. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in designing collaborative activities, facilitating communication, supporting knowledge construction, promoting self-regulated learning, and integrating real-world problem solving. Reflective practice, scenario-based exercises, and continuous professional development enhance understanding and readiness for the exam. By mastering these strategies, candidates are equipped not only to succeed in the exam but also to implement effective, technology-integrated instruction that supports meaningful learning outcomes in diverse classroom environments.
Advanced Strategies for Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 Exam
Preparation for the Microsoft 62-193 exam goes beyond basic understanding and requires advanced strategies to master scenario-based questions and real-world applications. Candidates must integrate knowledge of educational technology with pedagogical principles while demonstrating proficiency across all six content domains. Advanced strategies include analyzing complex classroom scenarios, synthesizing multiple concepts, and applying technology to solve problems efficiently. Candidates should focus on developing higher-order thinking skills and ensuring that technology integration supports meaningful learning outcomes.
Advanced preparation also emphasizes reflective practice. Candidates can maintain detailed logs of lesson plans, digital tool usage, and student engagement metrics. By analyzing the effectiveness of each approach, educators develop insights into optimizing learning experiences. This analytical process directly supports the application of knowledge in exam scenarios where multiple variables may influence outcomes.
Deep Analysis of the Six Content Domains
Understanding the six content domains in depth is crucial for excelling in the 62-193 exam. Facilitating student collaboration requires mastery of tools that enable group learning in both physical and virtual environments. Candidates should explore platforms that support synchronous and asynchronous collaboration, manage group roles effectively, and ensure equitable participation. Advanced strategies include designing multi-phase projects where students must negotiate tasks, integrate resources, and produce a collective outcome, all while using digital tools efficiently.
Facilitating skilled communication requires understanding how to enhance clarity, engagement, and accessibility through technology. Candidates should explore multimedia tools, digital presentation platforms, and collaborative writing applications. Techniques such as scaffolding digital presentations, peer review of online assignments, and providing structured feedback on communication tasks help students develop higher-level communication competencies.
Facilitating knowledge construction involves guiding students to critically analyze, synthesize, and apply information. Candidates can design inquiry-based projects, research assignments, and interactive simulations that require students to construct knowledge independently. Advanced strategies include incorporating data analysis tools, integrating real-world datasets, and using interactive platforms to support collaborative knowledge building. This approach encourages deeper engagement and critical thinking, which are essential for both classroom success and exam performance.
Facilitating self-regulation focuses on helping students manage their own learning. Candidates should explore digital goal-setting platforms, learning management systems with progress tracking, and reflective tools such as e-portfolios. Effective strategies include teaching students to monitor their achievements, evaluate their work, and adjust learning plans. Candidates preparing for the exam should practice creating assignments that require students to use these tools, as well as analyzing how self-regulated learning impacts outcomes.
Facilitating real-world problem solving and innovation requires designing learning experiences that connect classroom activities to authentic challenges. Candidates can simulate professional or community-based projects where students must apply knowledge, generate innovative solutions, and evaluate results. Advanced strategies involve scaffolding problem-solving processes, integrating interdisciplinary knowledge, and using digital tools to prototype solutions, conduct research, and present findings.
Facilitating student use of information and communication tools emphasizes ethical, effective, and purposeful technology application. Candidates must ensure students understand digital literacy principles, evaluate sources critically, and select appropriate tools for tasks. Advanced preparation includes creating assignments that require students to compare different digital platforms, analyze data accuracy, and communicate findings responsibly.
Implementing Scenario-Based Practice
Scenario-based practice is critical for mastering the 62-193 exam. Candidates should work through complex teaching situations that integrate multiple domains simultaneously. For example, a scenario might require designing a collaborative project that incorporates self-regulation, communication, and real-world problem solving. Practicing such integrated scenarios helps candidates develop the ability to analyze multifaceted challenges, apply technology strategically, and anticipate potential obstacles.
Simulation exercises enhance preparation by replicating classroom dynamics. Candidates can design digital lesson plans, monitor student participation, and adapt strategies in real time. These exercises help develop decision-making skills, improve familiarity with technological tools, and reinforce the application of theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. Scenario-based preparation also strengthens the ability to respond to unexpected challenges, which is a common feature of exam questions.
Leveraging Advanced Digital Tools
Proficiency in advanced digital tools is essential for both exam preparation and real-world application. Candidates should explore platforms that facilitate collaboration, communication, data analysis, and content creation. Examples include cloud-based collaborative workspaces, interactive multimedia tools, virtual labs, and data visualization software. Understanding the capabilities, limitations, and best practices for each tool enables candidates to integrate technology effectively into lessons and address diverse learning needs.
Candidates should also practice combining multiple tools to achieve instructional goals. For example, a collaborative project might use a cloud workspace for document sharing, a presentation tool for delivering findings, and a learning management system for assessment and feedback. Developing fluency in these integrated applications strengthens readiness for exam scenarios and enhances classroom effectiveness.
Advanced Assessment and Feedback Strategies
Assessment and feedback are central to the 62-193 exam and effective technology integration. Candidates should design assignments that allow for formative and summative evaluation using digital tools. Advanced strategies include incorporating automated feedback systems, peer assessment mechanisms, and real-time monitoring of student progress. Candidates should practice interpreting assessment data, providing constructive feedback, and adjusting instruction to meet learner needs.
Integrating assessment with lesson planning ensures alignment between learning objectives and evaluation methods. Candidates should explore methods for tracking student engagement, measuring skill development, and analyzing the impact of technology on learning outcomes. This analytical approach enhances preparation for exam questions that require critical evaluation of teaching strategies and instructional effectiveness.
Incorporating Reflective Practice in Preparation
Reflective practice is a key component of advanced preparation. Candidates should systematically document lesson planning, technology integration, and student engagement outcomes. Analyzing successes and challenges allows educators to refine strategies, improve decision-making, and strengthen understanding of digital pedagogy. Reflection also promotes adaptive teaching practices, ensuring candidates can respond to diverse student needs and dynamic classroom environments.
Reflective exercises might include evaluating the effectiveness of a collaborative project, assessing communication outcomes, and analyzing problem-solving activities. Candidates should maintain records of these reflections to support exam readiness and demonstrate professional growth.
Managing Exam Time and Developing Strategies
Effective time management is critical during preparation and the actual exam. Candidates should create a structured study schedule that balances theoretical review, scenario-based practice, and hands-on exercises. Simulating timed exam conditions helps develop pacing skills, reduce anxiety, and improve accuracy in responding to questions.
Developing a question strategy is also essential. Candidates should practice identifying key elements in scenario-based items, prioritizing responses, and managing complex multi-step problems. Time management strategies include allocating sufficient time for reading and analyzing scenarios, applying knowledge to generate solutions, and reviewing answers to ensure completeness and correctness.
Addressing Common Challenges in 62-193 Exam Preparation
Candidates often encounter challenges such as integrating multiple domains simultaneously, adapting to unfamiliar technology tools, and interpreting scenario-based questions accurately. Advanced preparation involves anticipating these challenges and developing strategies to overcome them. For example, practicing integrated lesson scenarios helps candidates manage multiple objectives at once, while experimenting with new tools builds confidence in technology usage.
Critical thinking and problem-solving exercises are particularly effective in addressing exam challenges. Candidates can analyze hypothetical classroom situations, identify potential issues, propose technology-based solutions, and evaluate outcomes. This approach ensures readiness for complex exam scenarios and reinforces the ability to apply knowledge in real-world contexts.
Continuous Professional Development for Exam Success
Continuous professional development supports both exam preparation and long-term instructional effectiveness. Engaging in workshops, webinars, and peer learning opportunities exposes candidates to new technologies, instructional strategies, and best practices. Staying informed about emerging tools and educational trends ensures that candidates can integrate technology effectively and adapt to changing classroom environments.
Professional development also strengthens exam performance by providing opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings. Candidates can document experiences, reflect on outcomes, and refine strategies for integrating technology across all content domains.
Integrating Interdisciplinary Learning Experiences
The 62-193 exam values the ability to connect technology with interdisciplinary learning. Candidates should practice designing lessons that integrate multiple subjects, encouraging students to apply knowledge across different areas. For example, a project could combine science research with digital communication skills, data analysis, and collaborative problem-solving. Integrating disciplines enhances critical thinking, creativity, and application skills while demonstrating the ability to leverage technology for comprehensive learning experiences.
Candidates preparing for the exam can simulate interdisciplinary projects, monitor outcomes, and refine instructional strategies. This preparation aligns with scenario-based exam questions and supports real-world teaching effectiveness.
Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 exam emphasizes advanced strategies, integrated lesson planning, domain-specific application, and scenario-based practice. Candidates must develop proficiency in designing collaborative activities, enhancing communication, supporting knowledge construction, promoting self-regulated learning, and facilitating real-world problem solving. Mastery of digital tools, reflective practice, time management, and interdisciplinary integration strengthens readiness for the exam and ensures effective technology integration in classroom instruction. By applying these advanced strategies, candidates are equipped to excel in the 62-193 exam and implement meaningful, technology-enhanced learning experiences that support student engagement, critical thinking, and lifelong learning.
Final Preparation Strategies for Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 Exam
Preparing for the Microsoft 62-193 exam requires a comprehensive and disciplined approach in the final stages of study. At this point, candidates should focus on consolidating their knowledge, refining application skills, and practicing scenario-based problem solving. The last phase of preparation emphasizes reinforcing the six content domains, ensuring mastery of educational technology concepts, and improving confidence in handling exam scenarios. Candidates should review prior lesson planning exercises, case studies, and simulation results to identify any remaining gaps in understanding.
In addition to reviewing content, candidates should dedicate time to practicing practical application. This includes creating integrated lesson plans that utilize multiple digital tools, designing collaborative projects, and implementing reflective activities to monitor student engagement. Emphasizing the connection between theory and practice strengthens readiness for scenario-based questions, which form a significant portion of the exam.
Enhancing Scenario-Based Problem Solving Skills
Scenario-based questions are a core component of the 62-193 exam. Candidates must develop the ability to analyze complex classroom situations, identify key challenges, and propose technology-supported solutions. Effective preparation involves practicing with realistic scenarios that integrate multiple content domains. For example, a scenario may require designing a collaborative research project that incorporates self-regulation, communication, and problem-solving skills.
Candidates should approach scenarios by first identifying learning objectives, then selecting appropriate tools and strategies, and finally evaluating potential outcomes. Documenting the reasoning behind each decision reinforces critical thinking and ensures that candidates are prepared to justify their approaches during the exam.
Mastering Time Management During the Exam
Time management is crucial for success in the 62-193 exam. Candidates should develop strategies for allocating sufficient time to each section, analyzing scenario-based questions, and reviewing responses. Practicing under timed conditions helps candidates become familiar with the pacing required to complete all questions accurately. Advanced strategies include skimming scenarios to identify key requirements, prioritizing responses based on complexity, and allowing time for review and reflection at the end of the exam.
Candidates can also simulate timed exam conditions using mock exercises and practice assessments. These exercises help identify areas where time management can be improved and build confidence in handling the pressure of the actual exam.
Reinforcing Knowledge Across the Six Content Domains
Mastery of the six content domains is essential for both exam success and real-world application. Candidates should systematically review each domain, focusing on advanced strategies and integration techniques. Facilitating student collaboration requires understanding complex group dynamics, leveraging digital tools to promote equitable participation, and designing multi-step collaborative activities. Practicing these strategies ensures readiness for exam scenarios that test collaborative skills.
Facilitating skilled communication emphasizes using digital media to support clear, engaging, and accessible interactions. Candidates should practice designing activities where students create multimedia presentations, participate in online discussions, and develop written communication skills. Understanding how to scaffold communication tasks and provide feedback strengthens preparation for the exam.
Facilitating knowledge construction requires supporting students in analyzing, synthesizing, and applying information. Candidates should practice designing inquiry-based projects, integrating data analysis tools, and creating interactive learning experiences that encourage knowledge building. Reflecting on these activities enhances understanding of effective instructional strategies.
Facilitating self-regulation focuses on helping students plan, monitor, and evaluate their learning. Candidates should explore tools such as digital goal-setting platforms, e-portfolios, and learning management systems. Creating exercises that require students to track progress and reflect on outcomes reinforces preparation for exam scenarios.
Facilitating real-world problem solving and innovation emphasizes connecting classroom learning to authentic challenges. Candidates should practice designing projects where students identify problems, propose solutions, and implement digital tools to evaluate results. Developing strategies for scaffolding these activities strengthens readiness for complex scenario questions.
Facilitating student use of information and communication tools requires guiding students in ethical, effective, and purposeful technology use. Candidates should practice designing lessons that incorporate source evaluation, responsible digital communication, and tool selection for specific tasks. These exercises enhance digital literacy skills and support exam readiness.
Utilizing Practice Tests and Mock Exams
Practice tests are a critical component of final preparation for the 62-193 exam. Candidates should engage in full-length mock exams to assess their knowledge, application skills, and time management. Mock exams provide insight into question formats, the complexity of scenarios, and areas requiring additional review. Reviewing performance after each practice test allows candidates to identify weaknesses and focus on targeted improvement.
In addition to content review, practice tests help build confidence. Candidates become familiar with the style of questions, the types of scenarios presented, and the expectations for responses. Repeated exposure to practice tests also reduces exam anxiety and enhances decision-making under time constraints.
Developing Critical Thinking and Analytical Skills
The 62-193 exam places a strong emphasis on critical thinking and analytical abilities. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to evaluate classroom scenarios, anticipate challenges, and implement effective technology-supported solutions. Developing these skills involves analyzing case studies, reflecting on lesson outcomes, and practicing scenario-based problem solving.
Candidates should practice breaking down complex scenarios into manageable components, identifying the most relevant information, and applying appropriate strategies. Documenting reasoning and evaluating the effectiveness of proposed solutions strengthens analytical skills and ensures preparedness for the exam.
Integrating Technology Across Diverse Learning Environments
Candidates must be adept at adapting technology integration strategies to different learning contexts. The 62-193 exam evaluates the ability to implement effective digital tools in traditional classrooms, blended environments, and fully online settings. Candidates should practice designing lessons that account for differences in access, student engagement, and collaboration opportunities.
Understanding accessibility considerations is also essential. Candidates should ensure that technology integration supports students with diverse learning needs, including those requiring assistive technologies or alternative content formats. This preparation ensures readiness for exam questions that assess inclusive instructional strategies.
Reflective Practices and Continuous Improvement
Reflective practice is a key component of final preparation. Candidates should maintain detailed records of lesson planning, technology integration, and student engagement outcomes. Analyzing successes and challenges allows educators to refine instructional strategies and strengthen understanding of effective digital pedagogy.
Reflective exercises may include evaluating collaborative projects, assessing communication outcomes, and analyzing problem-solving activities. By systematically reviewing these experiences, candidates develop a deeper understanding of how technology supports learning and can apply this knowledge effectively in the exam.
Advanced Assessment Techniques
Assessment is central to the 62-193 exam, and candidates should master advanced techniques for evaluating student learning. This includes designing assignments that incorporate formative and summative assessments, providing meaningful feedback, and analyzing performance data. Candidates should practice using digital tools for assessment, such as learning management systems, automated feedback platforms, and peer evaluation mechanisms.
Integrating assessment with lesson planning ensures alignment between learning objectives and evaluation methods. Candidates should analyze student performance data to adjust instructional strategies and improve learning outcomes. Practicing these techniques strengthens exam readiness and enhances instructional effectiveness.
Managing Stress and Exam Confidence
Exam preparation includes strategies to manage stress and build confidence. Candidates should develop a study routine that balances review, practice, and rest. Techniques such as mindfulness, focused breathing, and positive visualization can help reduce anxiety and improve concentration.
Simulating exam conditions also helps build confidence. Candidates should practice completing scenario-based exercises under timed conditions, reviewing answers, and reflecting on performance. Familiarity with the exam format and expectations reduces uncertainty and enhances performance on test day.
Applying Interdisciplinary and Real-World Connections
The 62-193 exam emphasizes the ability to connect learning across subjects and real-world contexts. Candidates should practice designing interdisciplinary projects where students apply knowledge from multiple domains to solve authentic problems. For example, integrating mathematics, science, and communication skills in a collaborative research project helps students develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Simulating real-world scenarios also strengthens exam readiness. Candidates can design projects that address community issues, professional challenges, or practical applications of classroom knowledge. This preparation enhances the ability to respond to scenario-based questions that assess real-world problem-solving skills.
Leveraging Peer Learning and Collaboration
Peer learning is an effective strategy for reinforcing knowledge and developing application skills. Candidates should engage in collaborative study sessions, share resources, and discuss challenging scenarios. This approach promotes deeper understanding, exposes candidates to diverse perspectives, and simulates the collaborative skills required in the classroom and assessed in the exam.
Collaborative preparation also helps candidates develop strategies for facilitating student collaboration. Practicing group activities, monitoring engagement, and providing feedback enhances both exam readiness and instructional effectiveness.
Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 exam emphasizes advanced strategies, exam mastery, scenario-based practice, and practical application. Candidates should focus on consolidating knowledge across the six content domains, developing critical thinking and analytical skills, integrating technology effectively across diverse learning environments, and refining assessment and feedback strategies. Practicing scenario-based exercises, engaging in reflective practice, managing time effectively, and participating in peer learning ensures comprehensive readiness for the exam. By applying these final preparation strategies, candidates are equipped not only to succeed in the 62-193 exam but also to implement technology-enhanced instruction that supports meaningful learning outcomes, student engagement, and lifelong learning in diverse educational contexts.
Final Words
Preparing for the Microsoft Technology Literacy for Educators 62-193 exam represents a significant step toward mastering the integration of technology in educational settings. Success in this exam requires more than memorizing facts or operating digital tools; it demands an understanding of how to apply technology strategically to enhance learning outcomes. Candidates must develop skills across six key domains, including student collaboration, communication, knowledge construction, self-regulation, real-world problem solving, and the effective use of information and communication tools.
Throughout preparation, combining theoretical knowledge with practical application is essential. Designing lesson plans, engaging in scenario-based exercises, and reflecting on instructional outcomes help candidates internalize concepts and develop a strong connection between digital tools and pedagogical goals. Practicing under simulated exam conditions, analyzing complex classroom scenarios, and refining decision-making strategies ensure readiness for the scenario-based questions that form a core part of the exam.
Additionally, candidates should focus on continuous professional growth. Staying current with emerging technologies, exploring new instructional strategies, and engaging in peer learning not only strengthens exam readiness but also enhances real-world teaching effectiveness. Emphasizing accessibility, ethical digital practices, and interdisciplinary learning ensures that technology integration is meaningful and inclusive for all students.
Ultimately, earning the Microsoft 62-193 certification demonstrates a professional’s ability to leverage technology to create engaging, innovative, and effective learning environments. It reflects a commitment to lifelong learning, adaptive teaching, and student-centered instruction. By approaching preparation strategically, practicing thoughtfully, and applying knowledge in realistic contexts, candidates can achieve success on the exam and translate that success into impactful teaching practices that benefit both educators and learners.
Microsoft MCE 62-193 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 62-193 Technology Literacy for Educators certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
- 98-388 - Introduction to Programming Using Java
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- MB-900 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals
Purchase 62-193 Exam Training Products Individually


Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 62-193 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 62-193 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 62-193 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 62-193 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 62-193 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 62-193. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 62-193 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 62-193 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 62-193 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 62-193 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!