Pass CompTIA Security+ Certification Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


SY0-701 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 611 Questions & Answers. Last update: May 02, 2025
- Training Course 167 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 1003 Pages

SY0-701 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 611 Questions & Answers
Last update: May 02, 2025 - Training Course 167 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 1003 Pages
Purchase Individually

Premium File

Training Course

Study Guide
SY0-701 Exam - CompTIA Security+
| Download Free SY0-701 Exam Questions |
|---|
CompTIA CompTIA Security+ Certification Practice Test Questions and Answers, CompTIA CompTIA Security+ Certification Exam Dumps
All CompTIA CompTIA Security+ certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are prepared by industry experts. CompTIA CompTIA Security+ certification practice test questions and answers, exam dumps, study guide and training courses help candidates to study and pass hassle-free!
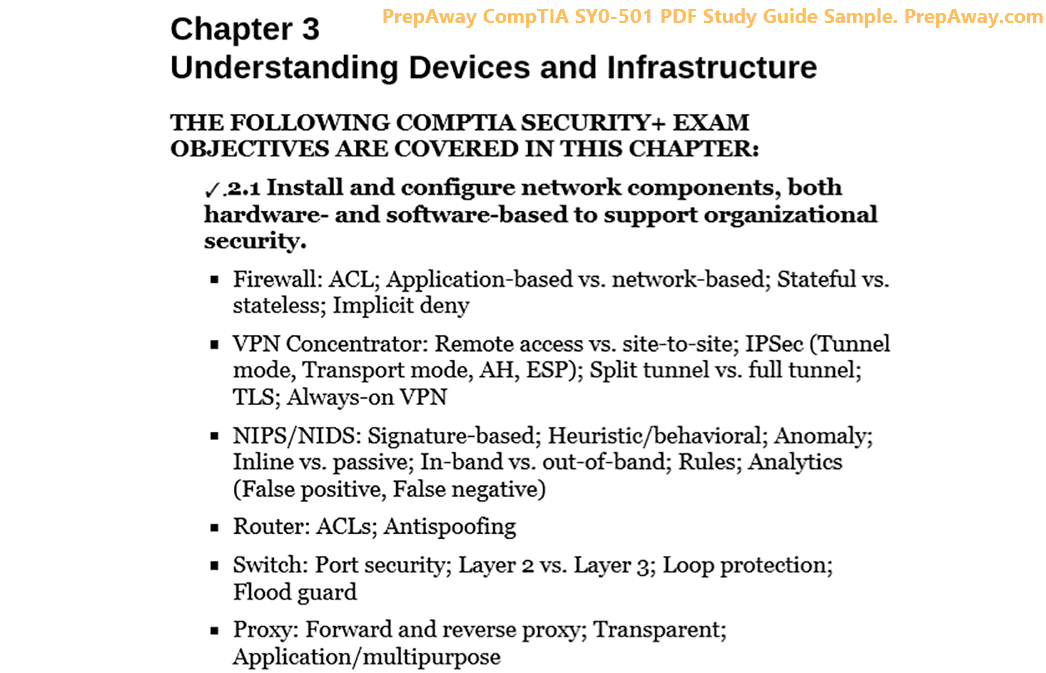
1.7 Techniques used in security assessments.
1. Threat hunting
In this video, we're going to be talking about threat hunting. So what exactly is this? Well, this is exactly what it says it is. It's hunting for threats in different places. We can go and find information about threats. Now, our exam does give us some futuristic things that we should know about this.
Let's get into it. So the first thing I have is intelligent fusion. Intelligent fusion, also known as fusion centres by some, This is where different agencies, such as different government agencies, the FBI, the NSA, the DoD, and of course different organizations, can combine to help gather and promote information sharing about threats that are happening currently in the environment. So if one organisation detects that there is some kind of threat going on or some kind of malware that is spreading, they can share information about it.
The other one here is threat feeding. Now, threat feeds—this is something that we went over before. Threat feeds are basically going to be places where you can find information about different threats and vulnerabilities out there. We talked about CVE; I think I mentioned this one in a previous video; Santa's intelligence is on this monitor. So here we go. So this will provide you with a very quick vulnerability of all the different vulnerabilities that are being reported as they emerge. So this one is from Pixar. If I click on this, it will tell you, "Okay, this one came out on November 12, and it's telling you more about it." So these are going to be feats of honour that are out there. Don't forget that these links are going to be in the description of the video.
You guys can check those out. Advisories and bulletins are another famous one. This is an interesting bulletin that you can follow. Bulletins are where we're going to have a lot of different vulnerabilities posted against them, very similar to a threat feed. So here I have the Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency, also known as CISA Gov. They have their bulletins, and they have weekly summaries like this vulnerability summary for the week of November 9. So this is a good bulletin that you can subscribe to. Don't forget that as a security professional, you should be up to date with the latest vulnerabilities and threats that are out there, and this is what this lesson is really showing you.
So they give the vulnerability summaries for the week, and then they go through the differences. So this is what I prefer to use over the TV website we discussed earlier this year; it gives me a quick summary. I can just spend a few minutes reading through it to see if there's something that's affecting, like Google Android. I'll probably go through some of these because they can affect my particular systems. But if it comes to technology that we're not using, we're probably not going to pay too much attention to it. So these are high-risk vulnerabilities that need to be fixed. And this is right off the bulletin. The final one is maneuver. So a manoeuvre is basically a series of movements used to find threats. This could be installing antivirus software on a computer. Installing intrusion detection systems on your system could be an example of this. Now, it can also be used by malware to avoid detection by the antiviruses that are out there. Remember that manoeuvre refers to the movement of the letter. You're doing it to stop threats, or it's a threat; stop doing it to avoid antivirus.
We'll come back later, of course, to talk more about how malware actually outmanoeuvres antivirus. Okay, so there are a couple quick things here that we need to remember for our exam. A couple of positives are that when it comes to "intelligence fusion," all it means is encouraging information sharing among various organisations and agencies. You should be signed up for a threat feed and bulletin. You have to know the latest vulnerabilities and threats to your organization. There may be a threat that comes out today that can have a drastic impact on your company. But because you weren't following these things, you didn't know about it. Now your company is severely vulnerable, and the company is dependent on you as the security professional to keep an eye on these things. So we must keep an eye on them.
2. Vulnerability scans
In this video, I'm going to be talking about vulnerability scans. Now, as a security professional, this is something that you're going to be using a lot. In this video, I'm going to show you guys a very popular vulnerability scanner that you can download download. It's called the Nexus Vulnerability Scanner. You can download it, use a trial version like the one I'm using here to scan a few machines, and then experiment on your own. So I suggest that you give it a shot because vulnerability scans are probably going to be one of the friendliest tools in your tool chest for managing security. Let's talk about this. So you are a security professional in an organization.
In some of the previous videos, we talked about things like CVE, which has all these vulnerabilities that are listed. Well, you can't keep up with that because there could be hundreds of vulnerabilities being posted every day. And you have so many systems—you have different versions of different software, different versions of Windows. This one didn't catch up to this day. That Mac over there, this Android, and that iOS device So many people simply run it. Then comes software and hardware—so many, so many different components—you can't keep up with it. So there are certain vendors that make software that archives all of these vulnerabilities into one big system.
You download it, run it, and it scans your network as well as the software and systems that are on it. It also informs you of the vulnerabilities in those specific systems. And now you can go ahead and fix it. This reduces your work a whole lot; think about this. If you have another person, imagine—let's put it this way. We have two ways of doing this. You could go and look at the CVE, find the vulnerabilities, and then determine whether they affect your system. Or we can have somebody else make software that has all these vulnerabilities. And then we can scan our computers to see if we're vulnerable to any of those threats or holes in our systems. This is a vulnerability scan, and there are quite a lot of these popular scans.
The Nexus security scanner and Koala's security scanner are some very popular ones. There's a free one called OpenVAS. That's a free one. Let's go take a look at some of them. And then I'm going to show you the one that I have installed. I've already run it because it takes a couple of minutes to run. So I'm going to show you how to run it so you can try it. I'm going to show you the end results that I've already gotten. Then we'll go over some things that are exempt just to be aware of them. Okay? So let's go to the browser here, and let's go to the browser here. And I'm going to show you guys one famous one: the Nexus scanner. So the Nexus scanner you guys have can just go and download this. They have a free version again. There are others; a couple of popular ones will be things like the OpenVAS Koalasecurity scanner, as well as some other popular ones. So here you go with the Nexus. It's worth noting that the Nexus Essential is completely free.
You can scan up to 16 IPs. As a Pen tester, I now use the Nexus Professional on a daily basis. This is something I'm highly familiar with. I've used it 100 times plus installed it on my computer, my notebook, and whatnot. But you don't need this one. This one is for businesses and your exam. You just need to know what vulnerability scanners are. And this is more than enough. So you could just go and download it, and it's going to open an installer, and you can just install it. Now I have it installed. Let's take a look at what it is, though. So I have it installed, and when it's installed, it's basically installed, and it brings up a web browser. It's basically in a web browser. Notice it's a local host, and it's running on port 88,34 on my computer. So when you install it, you have to create a username and password. So I created a username and password with Andy, and my password is password. Yeah, I don't really have the best password. You guys have probably seen it go with bad passwords.
So when it starts up, you're going to want to do a scan, right? You're going to want to see how the scan works. Now I'm going to show you how to set up a scan. I'm not going to run it because I've already run it. Now you can scan. Remember that this is more for your home network or a small business network. It only supports 16 computers. So I could go here if I want to set up a scan. So I would go to my scan. I'm going to say "new scan" and note all these interesting scans we have. So we can do a simple scan. This is going to find all the hosts and the open ports on those hosts. That's interesting. We're going to give that a shot really quickly. If you want to do a basic scan against hosts, you can do an advanced scan on a particular system. So you would select a particular scan if you just wanted to do a basic scan.
And then you would give it a name. So I gave it a name here. Let's say windows. My windows. Seven DM. Right. That's what I'm scanning. And then you want to go in here. You want to give it an IP address. You've got to know the IP address of what you're scanning. You would then click on "Save." Let's say. I've already got Windows 7 installed. It's verified my windows. 07:00 p.m. Here. So I think this is 175. Yes, it is 192-6175. And you just click "save." All right. Here are my windows. Seven. And when you want to scan it, you just click "launch," and it goes into this period where it's going to start to scan it. Now, I've already done this. This does take a while, all right? This could take some finesse, which I don't have in this video.
And I don't want to stand here and look at you when there's nothing going on for a minute. I'm going to stop this because I've already done it. I did it a while back. You can see it here today at 1154. and I'm just going to go ahead and click on it and notice. Now remember, this is a Windows 7 box that has a lot of vulnerabilities on it. It has 29 vulnerabilities in particular. and we could see that we have one that's critical. So if I go in here, these are high ones. You could see high vulnerabilities, like one of the high vulnerabilities they say I have; if I click on it, it will tell me what it is.
So it's saying that this thing here has an unsupported web server running. Now, I didn't install IIS on that machine to make it a website server. It's a really old version of IIS. And the good news, as the Nexus informs me—do you see this? It's actually telling me what to do. It's like, "Hey, go and remove that web server from there." Upgrade it if you want another web server because you're using a really old one. So that was something I thought was pretty cool about it. It can go in here. It will give you information about what's running on that particular system. Right? So we do have some vulnerabilities that I can go into here. There are some medium-sized vulnerabilities. We have some mixed-result vulnerabilities that are in here.
Now, this can take a while, all right, just to go through all these vulnerabilities. But generally, anything that you find that's going to be medium-high or critical, you're going to want to address it right away. and that could be anything. That could be user accounts without passwords. It could be an unpatched machine that is using a web server that has been hacked. So you can see how powerful this is. You can see that vulnerability scanners do a lot of the work that we should be doing with an automated scan. I mean, I could go to my Windows 7 box and try to find all vulnerabilities, but this wonderful tool can do it for us and comes with amazing reports. And with this, I'm going to go back here to my notes, and we have some things that our exam wants us to know about this.
So a couple of quick things: false positives and false negatives. A false positive occurs when it reports a vulnerability but there is none. When they tell you there is no vulnerability, this is a false negative. But there is one. One of the most important things to remember about vulnerability scans is to conduct thorough investigations. Investigate anything marked as a vulnerability, particularly a critical vulnerability. Generally, the scanners are going to be right, but do your investigations connect to the system? See what's wrong with it? See how you can fix it? And then sometimes you may discover that it's a false positive. The system is actually well secured, and the scanner just didn't pick that up. False negatives can be extremely dangerous because it is sin, there is nothing there, but there is. So this one, once again, is connected to systems.
Some people say to use multiple scanners. I don't know if that's a good idea. I mean, some people say it's okay. Different posts and articles you read said you should do that. I've never actually done that. I'm not going to recommend it. But some people say that if one scanner doesn't catch something, another might. Log reviews. One thing we could do for the vulnerability scans is review the logs in these scans as well as the logs in Windows. So the vulnerability scanner may state that there is a particular vulnerability, and you could go check out the login window to verify if it's there. Now, vulnerability systems like Nexus will have logs that you could review. Some scans will require credentials, while others will not. Now, deep scans, which are known as more intrusive scans that can get into the systems, will be credentialed, which means you're going to have to have some kind of admin privileges on those machines.
Nonintrusive scans like this Nexus scanner don't really require any admin privileges. It just scanned it. So in that one there, it didn't need any credentials. So credentials would mean that you'd need to have a username and a password to be able to get into that machine. But in truth, scans can give you a lot more information than a scanner from the outside. Vulnerability scans are available for particular applications. They are vulnerability scans that can only scan a specific app. Web scans can scan particular applications, web applications, and websites for particular problems. And then network scanners can scan an entire network of network devices. I'm going to show you guys a website that can do a web vulnerability scan. Now, I'm not going to run it, but if you know of a website that you want to run into, you could, because we need permission to run it. It's Pentestools. Okay. Pentest tools.com.
As a result, pentesttools.com I'm going to go here to tools, and we're going to say website scanner. You do, however, get two free scans here. So you would go in here and you would put in a link, right? You put in a URL. Now, I don't recommend doing this unless you have permission to work for an organization or have a personal Web site. You can put it here. This would then scan your personal website and notify you if it was vulnerable to cross-site scripting or SQL injections. Are there any errors that need to be fixed right away? If not, somebody can hack your website or DDoS your website. So this year there will be a website vulnerability scanner. There are ones for specific applications. Next is more like a network one. OK, we did talk about CVE previously. We'll just do a quick review of what CVE was. Notice how many times it comes up in the exam objectives here. So for your information, CVE Oops, I clicked on the wrong thing there. So with CVE, it's a listing of all the most up-to-date listings of vulnerabilities that are out there.
You can see that this thing is updated pretty quickly. This was updated an hour ago with different vulnerabilities that are out there. Okay? The other one I wanted to show you guys was this one called the Common Vulnerability Scoring System. And this is like a calculator. So when you see vulnerabilities, OK, they give you a score. And I'm going to take you back to a previous lesson where I showed you guys, Carlos. And then in here, when you click on different vulnerabilities, sometimes in these particular systems, you see what these vulnerabilities are. Depending on where you're looking, they may start to rank them. Now, how do they rank vulnerabilities? You get a listing of these vulnerabilities, and certain bulletins will actually give you a score.
So, like, look at this one here with the bulletins. If I go back to the bulletin, it's covered in my previous video. By the way, You notice the bulletin and the CVSS score. So notice, as I showed you, that one didn't really have it, but this one does. CD scores here. How would he get any scores? How can we use the scoring systems? That's what this is. So pay attention to Term, the Common Vulnerability Scoring System. You're working in security. You see that a vulnerability has just been posted against a particular site, and then you see a score. But how is it weighed? It reaches, I believe, a maximum of 9.8. But how is it weighed? How are they doing it? That's what this is.
This is a calculator that we could also use, not just them using it to rank the score, but you can see when something is a 920: why is it so high? Let me show you what I mean. So I'll use the calculators, which are essentially calculators. So I'm going to go in here and I'm going to say CVSS three-one. And I'm going to say, "Okay, I've got a vulnerability that I just discovered." It's a network attack. Because of its simplicity, it does not necessitate much. It doesn't need a lot of complexity to get done. It doesn't need any privileges to do it. It doesn't need any user interaction and doesn't change the scope of the network, but it steals all the data. It could modify all the information and bring down the network. Now watch the score. 9.8 is the worst score, right?
This is like a critical vulnerability. But if it didn't steal data, it goes down to nine one, non-confidentiality, right? If it didn't manipulate integrity, now it's down to 7.5. Watch what happens if you remove one of these. It's zero. So it has to affect one thing. Let's say it was a confidentiality attack that required high privileges. Now it's really low. Maybe it was a member. It was a very complicated event. It's 4.4. Maybe it was a physical thing. Now it's 3.8 versus a network attack. Maybe it was a local attack. You see how the scores are dropping there. So you could use this. There are additional options here that you can select and define regarding the specific vulnerability risk that you're looking at. So where would you use this?
Well, you would use this calculator, the Common Vulnerability Scoring System, to help you rank risk or vulnerabilities, right? And now you understand where the bulletins are getting them from: from highly trained security professionals that work within the CISA that rank the risk and put a score on it. So now you better understand. So, nine eight, there's a risk that stealing the data will bring down a system, change the integrity, and is simple to do. Okay? The last thing here about vulnerability scans is that you want to make sure you view your configurations. You want to ensure two things, two sets of configurations. You want to make sure the vulnerability scanner is configured correctly to look for the right one. Notice that we had a variety of different scans we could have selected. You want to make sure those are configured correctly. You want to make sure the hosts are configured correctly.
After the scan is done, you want to go back and reconfigure the systems, update the machines, and remove those vulnerabilities. You may want to run a scan after this to ensure that the vulnerabilities are fixed. So, like on my Windows system, I have 29 vulnerabilities. I should go fix it and see what's wrong with it. And then what I'm going to do is go back to it. I'm going to go back to it, and then I'm going to fix it. "Okay, so let's scan it, and maybe we can bring that number down one or two, or even hopefully to zero vulnerabilities," I'll say. Okay? We talked about something you should do in this video, and I hope you go out and practice. That is going to be a vulnerability scanner. I hope you guys go out and download the Nexus scanner, okay? And I want you guys to try it out and spend some time with it. Let it scan a VM of yours, because, trust me when I tell you this, this is a lifesaving tool.
This is a tool you guys are going to use a lot. Any time you install software or organizations, you're going to say, "Do you want a vulnerability scan on that?" Any time they manipulate or change things, once again, do you want a vulnerability scan? When you make changes and then run periodic vulnerability scans, keep in mind that it's not just for your network or a specific computer. You do these things for websites, too; vulnerabilities can save a lot of time in our organizations. It ensures that we can detect the latest vulnerability without having to do a whole lot of work. So since this thing saves us a lot of time and it's so great, go and give it a shot.
3. SIEM and SOAR
In this video, I'm going to be going over something called theme systems, or what's known as security information and event management. Also, some people call it Syslogs, and another one is called SOUR, which stands for Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response.
Now, quite a lot of things are there, but I'm going to explain to you guys why these systems are so badly needed for your exam. You don't need to get into it and configure it. You just need to know what it is. And I'm going to not just show you what it is, but I'm actually going to show you one and show you why we need it so badly. So let's start off with SEAM systems again, security information, and event management. So imagine you're working on a big network. You've got a couple of thousand devices.
You have hundreds of servers; you have hundreds of switches; you have routers, firewalls, and ID systems. Now, one of the things with these devices is that they are going to generate a lot of log files. Now remember, log files are important. Log files tell you if there are errors on the device, if there's intrusion on the device, or if they're just informational. things such as when people logged in, when they logged off, when they accessed this folder, when that application started, when it shut down, and so on. Analyzing log files is a critical part of managing security on any network.
The problem with this is that there are too many log files. As I sit here today, the organisation that you're working for, or the organisation you may be working for soon, generates hundreds of megs to gigabytes of data per minute in log information. So many entries. Check out your events viewer on your computer, and you'll see what I mean. And every time you log in, it generates a bunch of entries. Every time you access a file or start an application, What we need is a system to centralise the collection of this log information, give us the ability to analyse it, and for that system to have automated abilities to analyse these particular event logs that are coming in.
Then it could send us alerts, allowing us to set thresholds for when we want alerts for specific types of events. So instead of having the log files monitor each individual system on your network or host on your network, you're going to have this central system that goes on and captures the log information from all these devices. I think the biggest player in this game is a company called Splunk. Splunk. Splunk is one of the best-known theme systems out there, OK? They have certifications for it. A lot of big businesses use it. It's really expensive, but they do have a free one. and we're going to take a look at that right now. Now remember what this is. So this is a piece of software that you're going to give log information to. You can connect it to different devices, and it allows you to analyse the log files. Now there are so many options for what you can do with it.
They are all courses, and certifications are based on them. In this way, I just want to show you what it is and give you a really quick overview of it so you know what it is. That way, you can get past your exam. However, if you want to learn more about it, you can download the free version, as I did, and experiment with it. But keep in mind that it's not an easy piece of software to use. It does take time; however, there is a steep learning curve. But just the basics of it are pretty easy. Let's take a look at it. Please return to my slide. In a minute, I will have my Windows 10 box. So splunk, right? This is Splunk Enterprise. This is the free version. I'll show you guys what I mean. I'm just going to Google Splunk here, and we're going to go to Splunk. And, you know, this is their website here. But I'm going to go back here. I want to show you guys. Here we go. Free trials and downloads And you can go ahead and download Splunk for free.
They say it's a free sample of our core enterprise platform. And you can download this. Now the problem with this is that it only indexes up to 500 megs. When you first download You get the full features of it, and after 60 days it becomes less functional, but it still works. It is 500 megabytes, which is not a lot for big businesses. 500 megs. You can generate 500 megs of order logs very, very quickly. So you guys can download this. You would install it. It instals as a web browser. It's a web application on your computer. and it simply boots up. And this is what you get when it boots up and when you log in. This is how it appears in the interface. So just as quickly, I'm going to get the log files for this computer.
We're going to import it into Splunk. I'll show you some of the options and give you a quick analysis of how to analyse them. All right, so I'm going to go here. I'm going to right-click on the Windows Start button. We'll call it an event. Viewer. And we're going to go down here to the Windows logs. I'm going to export this. Here's my Windows log file. So the Windows security log files tell you things like when people logged in, right? So here's somebody logging in. Here's me logging in, and when people access documents or objects and whatnot, it'll store it. Now you can see that this thing has a lot of log files. So I'm going to right-click on this. We will say, "Don't filter, create." There's the export option. Save all event entries as, and we're going to save this on our desktops as the security events. I'm just going to give it a quick save there. Nope, that's fine. OK, so let's minimise this; make sure it's on my desktop. Here it is.
Alright, so I'm going to go back here to Splunk and I'm going to say "add data" because we'll analyse some data for it. Now, before I import the log files, I'd like to show you some of the data sources that come pre-built with it. So you could say cloud computing, and you could connect AWS directly to this thing. So you could pull the files, or you could connect Cisco's or Palo Alto's devices directly to it. So you would just select Cisco and follow the configuration, and it can actually grab the log files of the VPNs off your firewalls, like your ASA or Pix firewalls. Notice we also have you install Windows add-ons, and then you can get the Windows event logs from different Windows computers throughout your network. You do have some different security devices here, like Active Directory, which you can connect to for McAfee antivirus, and so on.
Endpoint for semantics, which you can all add in here. So I think that's pretty cool stuff. I just want to do a quick one with you guys. I'm going to click on "Upload," and we're going to click on "Select File." We're going to go to our desktop and double-click on this security event. Okay, so it was imported. We're going to go ahead and click on "next." Okay, that's fine. We're not going to change any of the other options in here, and we're going to click Submit. So it uploaded into it, and now we can start searching for it. So, now that they've brought it up, they're showing you some options for searching. Now you can just go in here, and if you're looking for very particular things, they have them.
So maybe I'm looking for the Andy account, and I just clicked "Search," and now it's finding all of the entry logs. It's in that log file that had Andy in it. Then you can even look for certain fields within it. And then you can filter photos, maybe a specific process, names, or perhaps here's a bunch of processes that I was accessing. So maybe I could look for this one here, where the log-on user interface is, and then it would filter for that also. and I can just see that.
That's really what this does, right? It allows you to learn through your log files, but it also has a whole bunch of automation and a whole bunch of ways for it to go out and grab the report and set up alerts. And it has its own algorithm to detect all types of interesting things. This is splunk. You can play around with it. I'm telling you guys, this is not an easy thing. It's very complex to use. It's like a whole certification. I personally know a guy who is certified, and Splunk has a certification in it. Okay, so now that we know exactly what these systems are, let's see what our exam wants us to know. So this is a theme system, or Syslog, to go ahead and grab all these log files, correct?
So they're going to have reports, and they have built-in reports where you can filter reports and see particular incidents that occur in the particular types of events you're looking for. They do packet capture. Some of them will do packet capture to capture information across your network. Data inputs would be how we're going to get the data in there. Notice how we can just upload an event zero file. Or notice the data connection that I was showing you. One of the things that sentiment analysis and user behaviour analysis can now show you if you capture log files is what the user behaviours are in the network. Are they more inclined to secure it? Are they setting up secure passwords? Are they always entering their password incorrectly? Sentiment analysis is going to look at their attitudes towards security on your network. This theme system is all about monitoring. It's all about security monitoring. Keep in mind that when people say "monitoring," they're talking log files, right? Logical monitoring—physical monitoring is looking at a camera, but logical monitoring is looking at log files.
And let's be really clear: we can't read log files. That's where you have software like this that can go out and read the log files for you. One of the good things is that it will capture the logs. It's a log collector. It has specific connection points that you configure in the software, and it basically aggregates all of these log files into one central system so that we can monitor and manage these log files. So-called thin systems are a sure thing in big businesses. I'll tell you that Splunk gets really expensive in large businesses because they charge a certain amount of money per data set. So large businesses will be paying a lot. But overall management of security is needed because who can read log files? Remember, there's no point in capturing log information about devices and software if no one is looking at them.
So you need something to look at them because, as humans, we don't want to do that. Okay, the second part here we're talking about is security orchestration and automation response sour in particular. So what this does is define three capabilities: threat and vulnerability management, security incident response, and security automation. security, operations, automation, and keyword automation. This is what this is going to specify.
So here's what I mean by this: In businesses today, you're going to have to have good and fast responses to security incidents. This can include data loss or theft as a result of vulnerabilities and threats entering your network. Why? Because the faster you respond to these particular systems, the faster they can get fixed. Remember, security that is left out there, breaches in your security, or holes in your network can have a drastic impact on your network.
This will allow companies to gather threat-related data from a range of different sources and, of course, automate these responses. This is what I keep telling you. Listen, you're going to have security incidents on every network you do. Some guys email per-person information. Your network has been hacked. The faster you react, the less damage you take.
The longer your response, the more damage there will be. Imagine if we had methods and processes in place, as well as software like these scene systems, to automate this for us, ensuring that we didn't lose information quickly. So the moment the incident happens, somebody responds. Correct. The incident reduces the impact on the organization. All right, so we just learned some interesting things about SEAS systems. I would tell you guys to download it, give it a try, and get yourself more familiar with it. Because if you're going to go work for those big businesses, you will see things like these particular systems.
CompTIA Security+ certification practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE files format by real users. Study and pass CompTIA CompTIA Security+ certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are the best available resource to help students pass at the first attempt.





I passed my exam with 780. Word of advice ,you need to study the content. The dump alone won't help you, premium dump . The dump will give you guidance and a feel of the exam, not all the questions are there. Make sure you go through the book and understand the content. This exam really tests your understanding don't under estimate it.
All the best.